Country Profile
 Trinidad and Tobago are the southernmost islands in the Caribbean Sea. Trinidad is 1,864 square miles in area, and Tobago is 116 square miles. At its closest point, Trinidad is some seven miles from the coast of Venezuela on the South American mainland. Trinidad is diverse geographically. It has three mountain ranges, roughly parallel to each other, running east to west in the north, central, and south parts of the island. The mountainous north coast is heavily wooded. The central part of the island is more flat and is where sugar cane is grown. The East–West corridor is an urban–industrial conurbation from Port of Spain, the capital, in the west to Arima in the east. San Fernando in the south is Trinidad's second city. The Point Lisas industrial park is nearby. Scarborough is the capital of Tobago. Afro-Trinidadians and other Creoles predominate in urban areas and in the north of Trinidad; Indo-Trinidadians live mostly in the central and south parts of the island.
Trinidad and Tobago are the southernmost islands in the Caribbean Sea. Trinidad is 1,864 square miles in area, and Tobago is 116 square miles. At its closest point, Trinidad is some seven miles from the coast of Venezuela on the South American mainland. Trinidad is diverse geographically. It has three mountain ranges, roughly parallel to each other, running east to west in the north, central, and south parts of the island. The mountainous north coast is heavily wooded. The central part of the island is more flat and is where sugar cane is grown. The East–West corridor is an urban–industrial conurbation from Port of Spain, the capital, in the west to Arima in the east. San Fernando in the south is Trinidad's second city. The Point Lisas industrial park is nearby. Scarborough is the capital of Tobago. Afro-Trinidadians and other Creoles predominate in urban areas and in the north of Trinidad; Indo-Trinidadians live mostly in the central and south parts of the island.
The official language is English. At present, Trinidad is multilingual, with inhabitants speaking standard and nonstandard forms of English, a French-based creole, nonstandard Spanish, and Bhojpuri.
Tobago, the sister island of Trinidad is located at the northeast of Trinidad. It is called "the land of the humming bird". Tobago is cool, serene and green and it has its lush tropical rain forests. It has a beauty that is enthralling and some very beautiful beaches. It is known for its oranges, grapefruits, mango, cocoa, breadfruit and copra. It is also known for its bird sanctuary with birds like the Scarlet Ibis, one of its most prominent. It is a place where Trinidadians and others come to avoid the hustling and bustling. It is a quiet romantic place for weddings and honeymoons. The southern part of the island is mountainous which allows for a beautiful scenic background. Tobago's capital is called Scarborough, which has a number of shops where tourists as well as the locals do their shopping.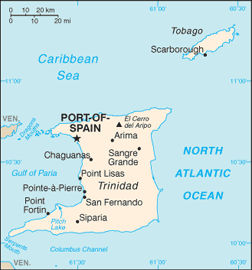
Christopher Columbus was the first European on record to have sighted Trinidad on his second visit in 1498. He called it La Isla de la Trinidad because of the three mountain peaks. Columbus did not actually land at Trinidad, but the subsequent Spaniards who came after him, enslaved many of the Amerindian inhabitants and carried them to the South American colonies. Spain was very interested in gold from Mexico (New Spain) and the gold from the Incas of Peru. Spain, therefore only paid very little interest in Trinidad, which did not have the precious minerals. It was not until 1592 before Spain established their first settlement at San Josef, which is located just east of Port of Spain, Trinidad's capital.
Britain took over the islands from the Spanish in 1797. The islands' sugar industry was hurt by the emancipation of the slaves in 1834. Manpower was replaced with the importation of contract laborers from India between 1845 and 1917, which boosted sugar production as well as the cocoa industry. The discovery of oil on Trinidad in 1910 added another important export. Independence was attained in 1962. The country is one of the most prosperous in the Caribbean thanks largely to petroleum and natural gas production and processing. Tourism, mostly in Tobago, is targeted for expansion and is growing.
